New Photos Reveal What’s Left Behind When a Rocket Travels to Space
Michael Soluri captures these strangely evocative traces of America’s heroic extraterrestrial journeys
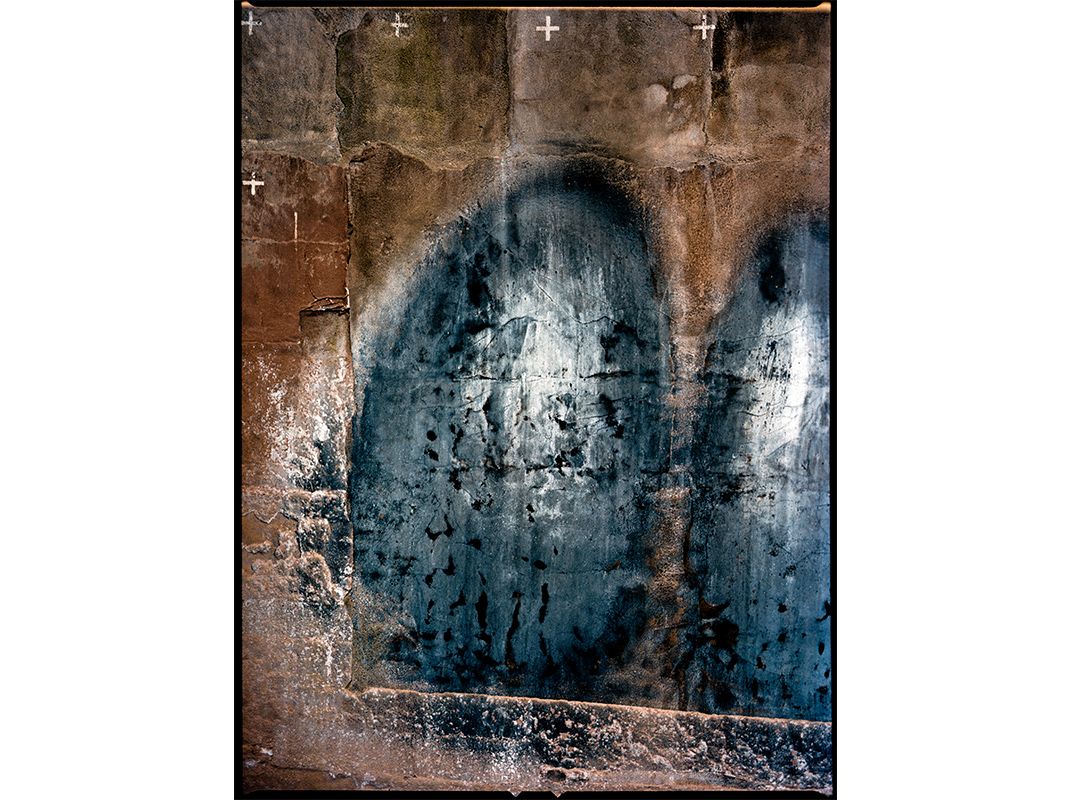
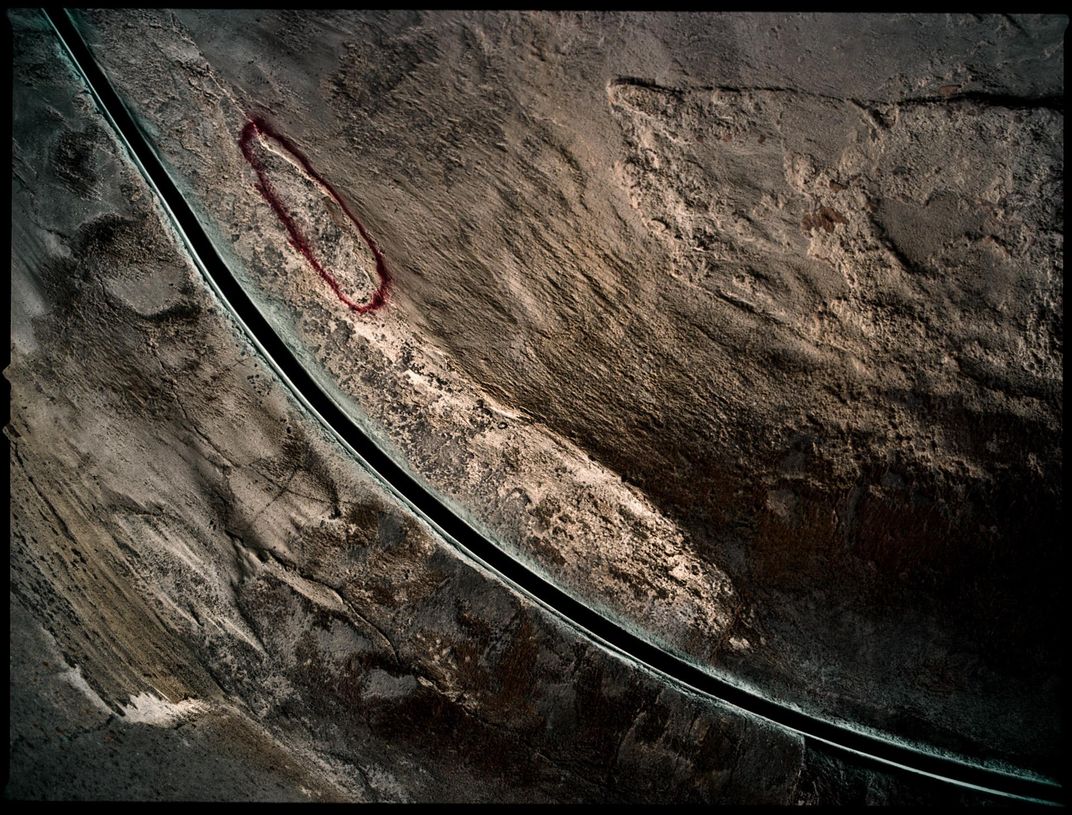
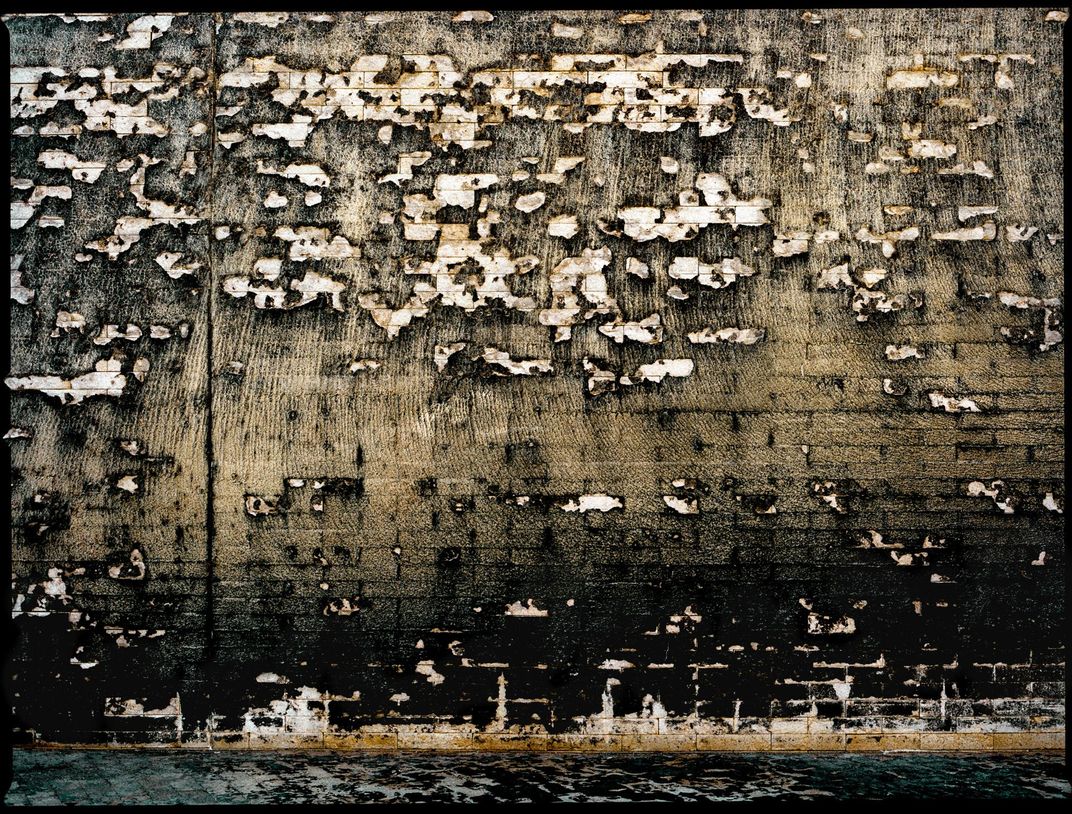
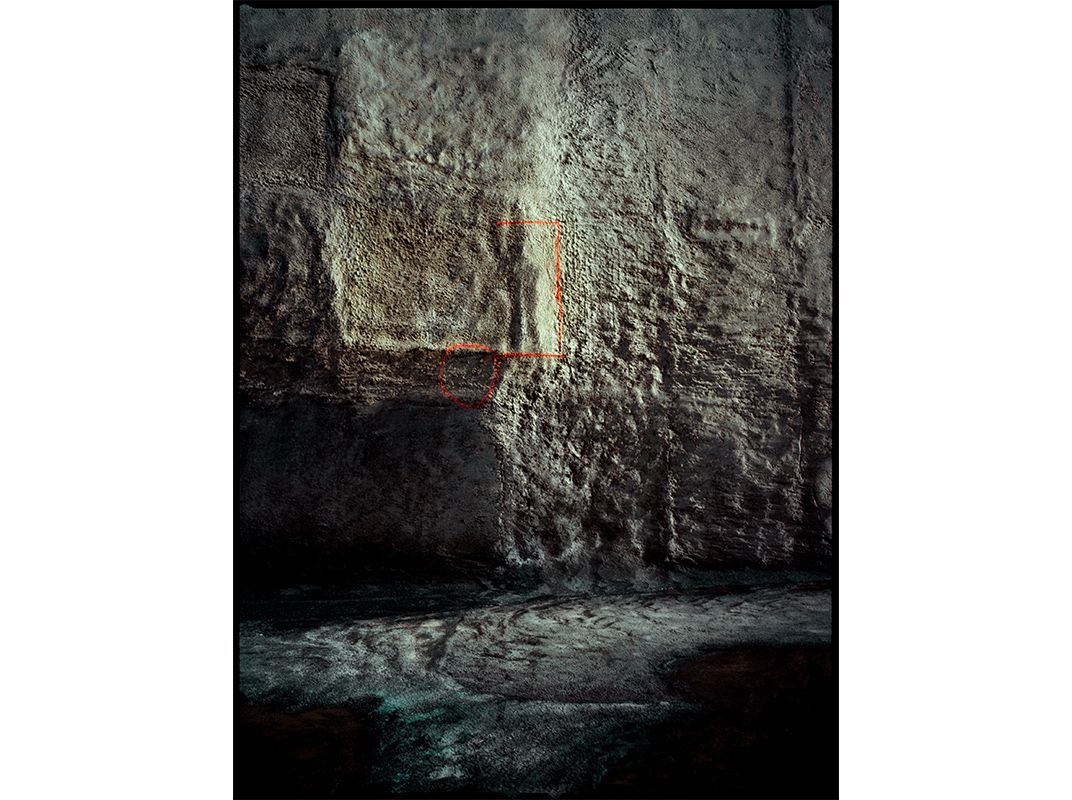
Deep within NASA’s Kennedy Space Center lies an enormous complex, Launch Pad 39A. It’s where Apollo astronauts began their journeys to the Moon and many space shuttle missions began, too. Each mighty blastoff left traces on the flame trench, a 42-foot-deep pit lined with fire-resistant bricks and concrete that channels a rocket’s superheated exhaust away from the spacecraft. Michael Soluri, a veteran space-exploration photographer and author of Infinite Worlds, about a 2009 shuttle mission, became fascinated by this scorched palimpsest, seeing it as reminiscent of another great human achievement—Paleolithic cave art. After NASA leased 39A to SpaceX, the company refurbished the flame trench. “I’m sad the marks aren’t there anymore,” Soluri says, “but I’m glad that I documented this evidence of the machines that took man into space.”
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/amy.png)



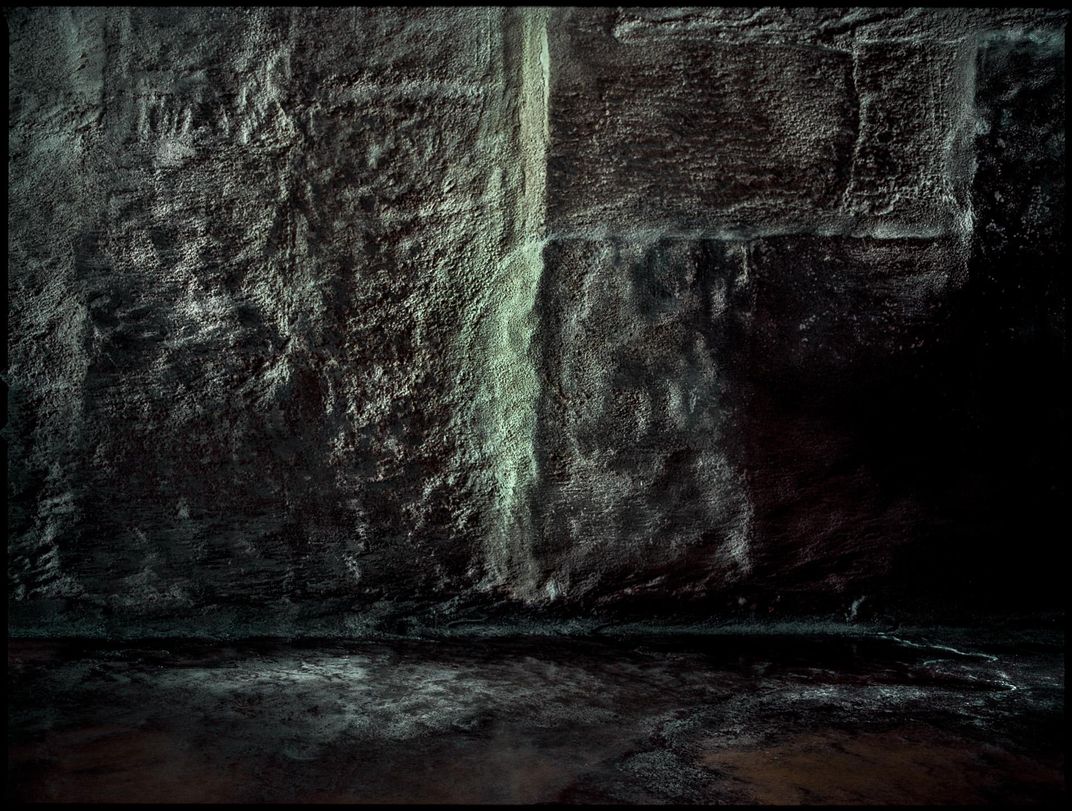


/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/amy.png)