Neuroscience
This 19th-Century 'Toy Book' Used Science to Prove That Ghosts Were Simply an Illusion
"Spectropia" demystified the techniques used by mediums who claimed they could speak to the dead, revealing the "absurd follies of Spiritualism"
See 15 Mesmerizing Photos of Hidden Scenes Only Visible Through a Microscope
Winners of the Nikon Small World Photomicrography Competition captured insects, cancer cells, cat claws and more
Seeing Vermeer’s 'Girl With a Pearl Earring' in Person Stimulates the Brain More Than Looking at Reprints, Study Suggests
Scientists used EEG headsets, MRI machines and eye trackers to study volunteers' responses to five paintings housed at the Mauritshuis museum in the Netherlands
Scientists Unveil the First-Ever Complete Map of an Adult Fruit Fly's Brain, Captured in Stunning Detail
The brain diagram, called a connectome, could revolutionize researchers' understanding of the human brain, which has many parallels with a fruit fly's
Everything You Wanted to Know About the Longest Nerve in the Body
Like a highway system, the vagus nerve branches profusely from your brain through your organs to marshal bodily functions, including aspects of the mind such as mood, pleasure and fear
New Hampshire Resident Dies From Rare but Serious Mosquito-Borne Illness
It's one of four cases of Eastern equine encephalitis reported in the U.S. so far this year—and the state's first since 2014
Weight Loss and Diabetes Drug Could Slow Alzheimer's Progression, Preliminary Study Suggests
In a year-long trial, people who received a daily injection of liraglutide showed an 18 percent lower cognitive decline than people who received a placebo
MDMA Treatment for PTSD Fails to Secure Federal Approval
One day after the FDA declined to approve the psychedelic for medical use, a journal retracted three studies of MDMA-assisted therapy due to unethical conduct by researchers
Alzheimer's Blood Test Outperforms Standard Diagnostics in New Study
The blood test accurately diagnosed Alzheimer's around 90 percent of the time, compared to 73 percent for specialists and 61 percent for primary care physicians
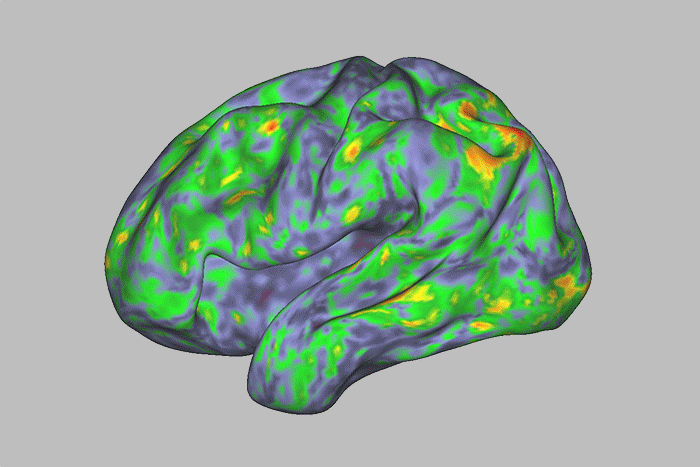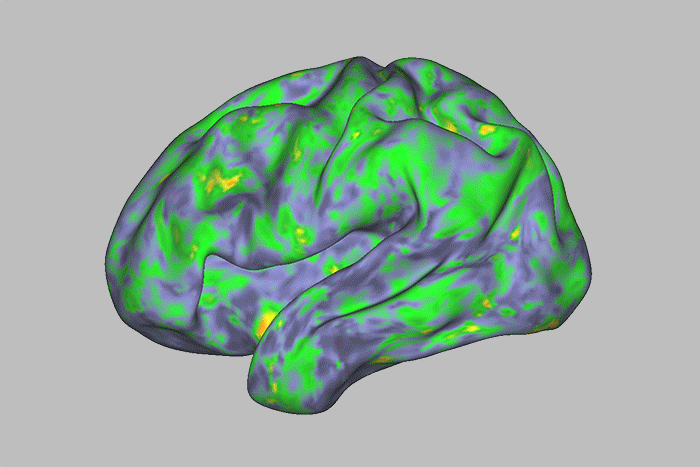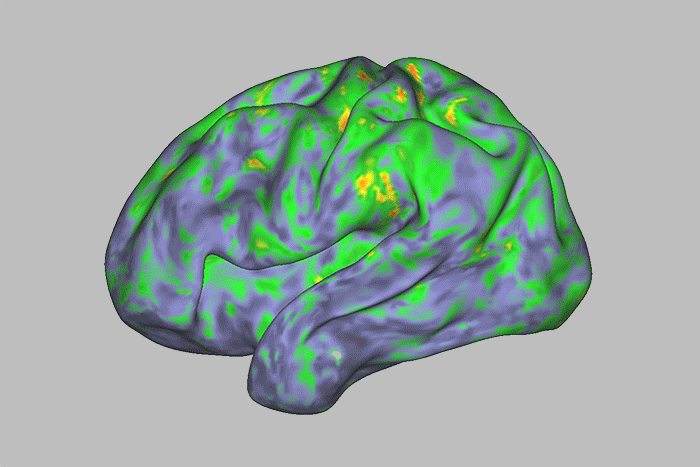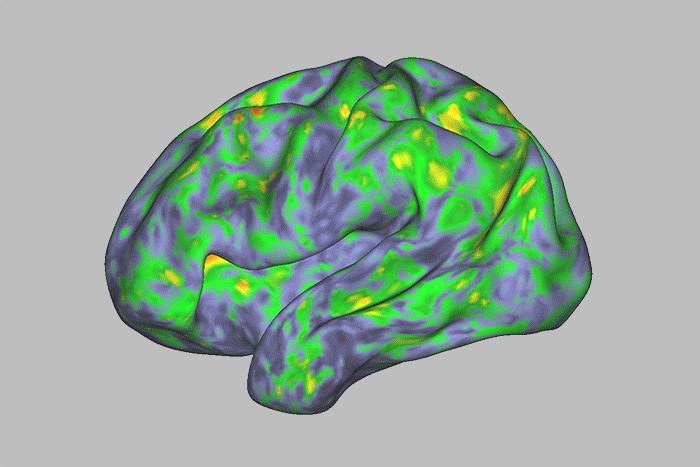
See How the Brain Responds to Psychedelic 'Magic Mushrooms'
A new study mapped large, temporary changes in brain areas related to introspection and one's sense of self, after participants took a dose of the drug psilocybin
New Blood Test for Predicting Parkinson's Disease With A.I. Shows Promise, Study Suggests
In preliminary research, scientists identified eight protein anomalies in the blood of patients with Parkinson's, which they say can help diagnose the disease up to seven years before symptoms appear
Can Virtual Coworking Platforms Make Us More Productive?
Membership services like Flow Club, Flown and Caveday offer online study halls complete with proctors and goal setting
Why Do Humans Sing? Traditional Music in 55 Languages Reveals Patterns and Telling Similarities
In a global study, scientists recorded themselves singing and playing music from their own cultures to examine the evolution of song
Scientists Imaged and Mapped a Tiny Piece of Human Brain. Here's What They Found
With the help of an artificial intelligence algorithm, the researchers produced 1.4 million gigabytes of data from a cubic millimeter of brain tissue
Are Days Passing Too Quickly? Memorable Experiences Might Help Dilate Your Sense of Time, Research Suggests
How we process time is linked to things we see, according to a new study, which found memorable, non-cluttered imagery can make moments seem to last longer
Almost All People With Two Copies of This Genetic Variant Develop Signs of Alzheimer's Disease, Study Finds
The research focused on a variant called APOE4 and largely looked at people of European ancestry—risk levels are different for other groups, the authors say
Researchers Breed Mice With Hybrid Brains Containing Cells From Rats
In one experiment, rat neurons helped mice restore their senses of smell—the first time any animal has perceived the world through the sensory hardware of another species
How Intelligent Was T. Rex? Scientists Suggest the Dinosaurs Were Like 'Smart, Giant Crocodiles'
A new paper refutes the idea that T. rex was as brainy as a baboon, furthering the debate on the extinct reptile's intellect
Scientists Translate Sleeping Birds' Silent Songs Into Sound—and They May Have Recorded a Nightmare
Using surgically implanted electrodes and modeling, researchers brought to life the vocal muscle activity of sleeping great kiskadees
Why Do Some People Always Get Lost?
Research suggests that experience may matter more than innate ability when it comes to a sense of direction
Page 1 of 18
:focal(700x527:701x528)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e6/85/e6857995-afdc-4779-aef2-1da3509affdf/spectropia.jpg)
:focal(1500x1000:1501x1001)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/6d/62/6d629d28-350a-448e-bab4-65c20048ffba/iod_-_2024_knop_daniel_e33042_f21773.jpg)
:focal(960x617:961x618)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/4e/7b/4e7b9fe3-d468-479c-890c-57c311720c06/girl-with-pearl.jpg)
:focal(1440x960:1441x961)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/b1/25/b12582c3-4fdf-4447-9938-41a2fb15bb60/fw_all_l.png)
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/37/c0/37c0b833-783b-435a-8356-c1d526539247/main_vagusnerve-crsallycaulwell-lede_web.jpg)
:focal(3140x2093:3141x2094)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/93/88/9388ea77-b284-47e4-97b6-83cfa256e72a/gettyimages-1927045430.jpg)
:focal(2500x1667:2501x1668)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/8a/d6/8ad64075-57a2-4239-93d4-6baf3489bedd/gettyimages-1793641166.jpg)
:focal(2667x1791:2668x1792)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/9c/d9/9cd992fa-e98f-4d96-adbd-2a80e6efb7ee/gettyimages-129369648.jpg)
:focal(1061x707:1062x708)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/24/2f/242f7b45-9432-4e4d-9deb-1beb7c4845a9/gettyimages-1443155227.jpg)
:focal(1061x707:1062x708)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/71/67/71670cf2-6c5d-41c2-a41b-1ba60b600e07/gettyimages-1348149832.jpg)
:focal(2048x1375:2049x1376)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/2d/97/2d970291-2df5-4f27-85aa-851bca5869b4/flowclubonlaptop.jpg)
:focal(512x288:513x289)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f6/96/f696d107-a38b-4554-be99-d0089e6a4128/music1.jpg)
:focal(1664x1093:1665x1094)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/c7/ba/c7baacef-cb16-4351-bd03-27bd56c1b461/connectomics2024-1-excitatoryneuronsoriginal.png)
:focal(1500x943:1501x944)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/d8/73/d873f475-0061-4cf6-a677-a74c62e328e3/50368695116_85e24b80b8_o.jpg)
:focal(1815x1210:1816x1211)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e7/0a/e70a08dc-1ec3-4c16-8f62-bccfa20435da/gettyimages-151036433.jpg)
:focal(2808x1872:2809x1873)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/3f/9a/3f9a09b9-6c57-4354-827f-6f45f25bb0dd/gettyimages-1234160574.jpg)
:focal(1024x683:1025x684)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/54/b1/54b11c8a-cce4-43fd-83b9-41ce0bd64ec8/juvenile_t_rex_at_carnegie_museum_of_natural_history_2013-12-14.jpg)
:focal(1023x565:1024x566)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/b3/fd/b3fd9f54-e937-4b9b-99f4-47ec00f4667c/40921799543_cd5d77e374_k.jpg)
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/07/20/0720406e-51f0-4bee-b91a-34b050bf3886/navigation-3200x1200_web.jpg)