America’s First Great Global Warming Debate
Thomas Jefferson and Noah Webster argue over conventional wisdom that lasted thousands of years
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/global-warming-debate-Thomas-Jefferson-Noah-Webster-631.jpg)
As the tumultuous century was drawing to a close, the conservative Yale grad challenged the sitting vice president’s ideas about global warming. The vice president, a cerebral Southerner, was planning his own run for the presidency, and the fiery Connecticut native was eager to denounce the opposition party.
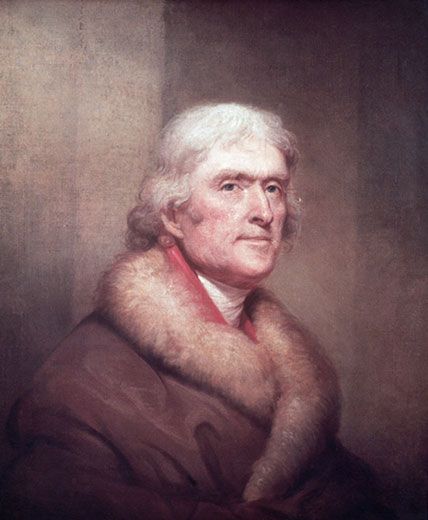
The date was 1799, not 1999—and the opposing voices in America’s first great debate about the link between human activity and rising temperature readings were not Al Gore and George W. Bush, but Thomas Jefferson and Noah Webster.
As a gentleman farmer in Virginia, Jefferson had long been obsessed with the weather; in fact, on July 1, 1776, just as he was finishing his work on the Declaration of Independence, he began keeping a temperature diary. Jefferson would take two readings a day for the next 50 years. He would also crunch the numbers every which way, calculating various averages such as the mean temperature each month and each year.
In his 1787 book, Notes on the State of Virginia, Jefferson launched into a discussion of the climate of both his home state and America as a whole. Near the end of a brief chapter addressing wind currents, rain and temperature, he presented a series of tentative conclusions: “A change in our climate…is taking place very sensibly. Both heats and colds are become much more moderate within the memory of the middle-aged. Snows are less frequent and less deep….The elderly inform me the earth used to be covered with snow about three months in every year. The rivers, which then seldom failed to freeze over in the course of the winter, scarcely ever do so now.” Concerned about the destructive effects of this warming trend, Jefferson noted how “an unfortunate fluctuation between heat and cold” in the spring has been “very fatal to fruits.”
Jefferson was affirming the long-standing conventional wisdom of the day. For more than two millennia, people had lamented that deforestation had resulted in rising temperatures. A slew of prominent writers, from the great ancient naturalists Theophrastus and Pliny the Elder to such Enlightenment heavyweights as the Comte de Buffon and David Hume, had alluded to Europe’s warming trend.
A contemporary authority, Samuel Williams, the author of a 1794 magnum opus, The Natural and Civil History of Vermont, had studied temperature readings at several points in the 18th century from his home state and half a dozen other locales throughout North America, including South Carolina, Maryland and Quebec. Citing this empirical data, Williams claimed that the leveling of trees and the clearing of lands had caused the earth to become warmer and drier. “[Climate] change…instead of being so slow and gradual, as to be a matter of doubt,” he argued, “is so rapid and constant, that it is the subject of common observation and experience. It has been observed in every part of the United States; but is most of all sensible and apparent in a new country, which is suddenly changing from a state of vast uncultivated wilderness, to that of numerous settlements.”
This opinion had been uttered for so long that it was widely accepted as a given—until Webster. Today Webster is best known as the author of the American Dictionary of the English Language (1828), but his “great book” was actually his retirement project. He was a pioneering journalist who edited American Minerva, New York City’s first daily newspaper in the 1790s, and he weighed in on the major public policy issues of the day, cranking out essays on behalf of the Constitution, a 700-page treatise on epidemics and a condemnation of slavery. He would also serve in the state legislature of both Connecticut and Massachusetts. Webster disputed the “popular opinion that the temperature of the winter season, in northern latitudes, has suffered a material change” in a speech before the newly established Connecticut Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1799. Several years later, Webster delivered a second address on the topic. The two speeches were published together in 1810 under the title “On the Supposed Change of in the Temperature of Winter.”
With the thermometer still a relatively recent invention—the Polish inventor Daniel Fahrenheit didn’t develop his eponymous scale until 1724—conclusions about weather patterns before the mid-18th century were based largely on anecdotes. In the first two-thirds of his 1799 speech, Webster attacked Williams, a pastor who helped found the University of Vermont, for his faulty interpretations of literary texts such as the Bible and Virgil’s Georgics. Challenging Williams’ assumption—derived from his close examination of the Book of Job—that winters in Palestine were no longer as cold as they used to be, Webster declared, “I am really surprised to observe on what a slight foundation, a divine and philosopher has erected this theory.” But Webster, while acknowledging that the Bible may well not have been “a series of facts,” tried to spin the weather imagery in ancient texts his own way. Citing passages from Horace and Pliny, Webster asserted that “we then have the data to ascertain the ancient climate of Italy with great precision.”
To settle the scientific debate, Webster offered more than just literary exegesis. In examining “the cold of American winters,” Webster focused on the numbers—and his opponents’ lack of hard data (Jeffersons recorded his own temperature readings in a private diary). “Mr. Jefferson,” Webster stated, “seems to have no authority for his opinions but the observations of elderly and middle-aged people.” Webster saved most of his ammunition for Williams, who had written the more extensive brief, replete with an array of temperature readings. Williams’ central contention, that America’s temperature had risen by 10 or 12 degrees in the prior century and a half, Webster asserted, just doesn’t make any sense. “The mean temperature of Vermont,” he writes, “is now 43 degrees…If we suppose the winter only to have changed, and deduct one half the supposed abatement, still the result forbids us to believe the hypothesis. If we suppose the heat of summer to have lessened in the same proportion…the summers formerly must have been intolerable; no animal could have subsisted under ten degrees of heat beyond our present summer temperature. On whichever side we turn our eyes, we meet with insurmountable difficulties.”
Webster concluded by rejecting the crude warming theory of Jefferson and Williams in favor of a more subtle rendering of the data. The conversion of forests to fields, he acknowledged, has led to some microclimatic changes—namely, more windiness and more variation in winter conditions. But while snow doesn’t stay on the ground as long, that doesn’t necessarily mean the country as a whole gets less snowfall each winter: “We have, in the cultivated districts, deep snow today, and none tomorrow; but the same quantity of snow falling in the woods, lies there till spring….This will explain all the appearances of the seasons without resorting to the unphilosophical hypothesis of a general increase in heat.”
Webster’s words essentially ended the controversy. While Jefferson continued to compile and crunch temperature data after his retirement from the presidency, he never again made the case for global warming. Neither did Williams, who died a few years after the publication of Webster’s article. Webster’s position was considered unimpeachable. In 1850, the acclaimed German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt declared that “statements frequently advanced, although unsupported by measurements, that…the destruction of many forests on both sides of the Alleghenys has rendered the climate more equable…are now generally discredited.”
And there the matter rested until the second half of the 20th century, when scientists began to understand the impact of greenhouse gases on the environment. The second great global warming debate poses a different set of scientific questions from those raised in the late 18th century, and this time the science clearly supports the idea that human activity (including clearing and burning forests) can increase temperatures. But it is Webster’s papers, with their careful analysis of the data, that have stood the test of time. Kenneth Thompson, a modern environmental scientist from the University of California at Davis, praises “the force and erudition” of Webster’s arguments and labels his contribution to climatology “a tour de force.”
Joshua Kendall is the author of The Forgotten Founding Father: Noah Webster’s Obsession and the Creation of an American Culture (Putnam, 2011).